Benefits for Auckland
An Auckland specific pathway will enable:
- early insights for decision makers to improve efficiency and future proof infrastructure investments
- information sharing to encourage demand flexibility through collaboration.
- coordinating infrastructure and streamlining electricity demand for the future
- a full view of biomass resource availability alongside a range of practical considerations – such as regional supply, transportation, site limitations, and regulatory factors.
About the Auckland RETA
A total of 195 sites spanning the industrial and commercial sectors are covered by the Auckland Regional Energy Transition Accelerator (RETA). These sites either have process heat equipment larger than 500 kW or are sites for which EECA has detailed information about their future possible fuel choices. Collectively as at 2022, these sites consume 10,600TJ of process heat energy, primarily from piped fossil gas, and produce 570 kt per year of CO2e emissions.
Auckland’s energy profile is diverse, including a relatively high proportion (compared to other regions) of sites that require very high temperature heat (>450oC). This report explores a range of technical options to improve efficiency, fuel options, and support more robust, future-ready energy systems tailored to the operational requirements of different industries. Both biomass and electricity are considered as fuel sources.
Energy efficiency and heat pump projects are also important for reducing energy consumption and right sizing boiler investment.
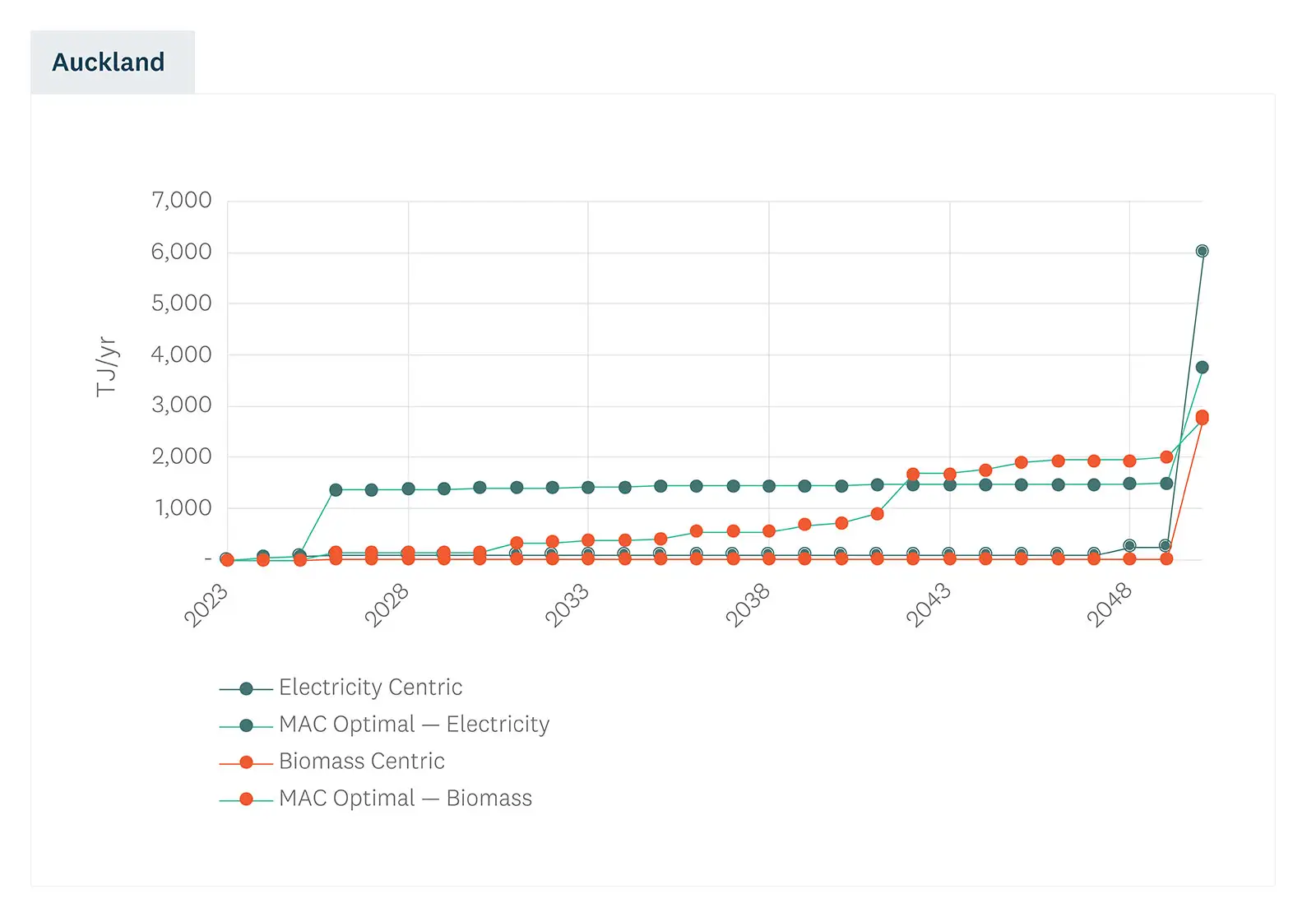
The report explores a range of scenarios that show how the timing and magnitude of renewable fuel uptake in the region might change based on different decision-making criteria. This analysis shows how the combined decisions of process heat users may provide both challenges and opportunities for the development of supply side infrastructure for biomass and electricity.
Across the sites, 505 potential individual projects covering demand reduction, heat pumps and future fuel options were analysed. The marginal abatement cost or 'MAC Optimal' pathway sees fuel decisions that result in 42% of industrial energy needs being supplied by electricity and 58% supplied by biomass.
Insights explored in the Auckland report
- The forecasts and mapping of regional stationary heat energy demand alongside renewable energy supply assessments.
- How the pathways are sensitive to changes in fuel prices.
- The importance of complementary strategies such as energy demand reduction, load flexibility, and the use of energy storage technologies to manage peak usage.
- Timeframes for different pathway scenarios:
The business as usual or ‘BAU’ pathway, which uses actual project timing or, for the majority of projects where timing is not known, is the slowest path.
The ‘MAC’ optimal pathway suggests 46% of fossil fuel reliance can be reduced by projects that are economic now.
- What the options are for industry to enhance efficiency and resilience with advanced technologies, cleaner fuels, and tailored energy systems.
Explore the RETA dashboard to view integrated insights on regional process heat fuel demand sites, biomass potential, and energy transition opportunities across New Zealand.
Read the report
Download the Auckland RETA report and discover the regional benefits of taking a regional approach to fuel choices and demand reduction.
Spare Electrical Capacity and Load Characteristics [PDF 17 MB]
Supplementary Electricity Information - GXPs [PDF 18 MB]
Supplementary Electricity Informaiton - Counties Energy [PDF 3.6 MB]
Auckland businesses face key energy decisions now and in the near future. Working together and aligning technology, infrastructure, and operations to advance a more efficient, resilient energy future.
Next steps
EECA’s national RETA programme is nearing completion with only the Wellington region yet to be finished.
We are happy to hear from anyone wanting to support the implementation of recommendations in the Auckland RETA report.Email RETA@eeca.govt.nz with any questions.
For more information on the RETA programme and the individual regions which have been included, visit the page below.