Benefits for North Canterbury
A North Canterbury specific decarbonisation pathway will enable:
- A view of biomass resource availability and the potential volumes, costs and demand for bioenergy.
- Early insights for decision makers to improve efficiency and future proof infrastructure investments.
- Best use of information sharing to encourage demand flexibility through collaboration.
- Demand for fuel suppliers and technology providers to provide the confidence for accelerating the development of new supply chains or capacity building initiatives.
About the North Canterbury RETA
A total of 80 sites – spanning the dairy, meat, industrial and commercial sectors are covered by the North Canterbury RETA. These sites either have process heat equipment larger than 500kW or are sites for which EECA has detailed information about their decarbonisation pathway. Collectively, these sites consume 4,267TJ of process heat energy, primarily from coal, and currently produce 372kt per year of CO2e emissions. RETA aims to eliminate as much of these process heat emissions as possible.
The focus of the North Canterbury report – the culmination of phase one of the RETA programme, is the fuel switching decision and the key role demand reduction plays in enabling fuel switching. Both biomass and electricity are considered as potential fuel sources.
RETA also recognises the importance of efficient demand reduction and thermal efficiency measures for reducing energy consumption and right sizing the boiler investment, which in turn affects decision-making around fuel switching.
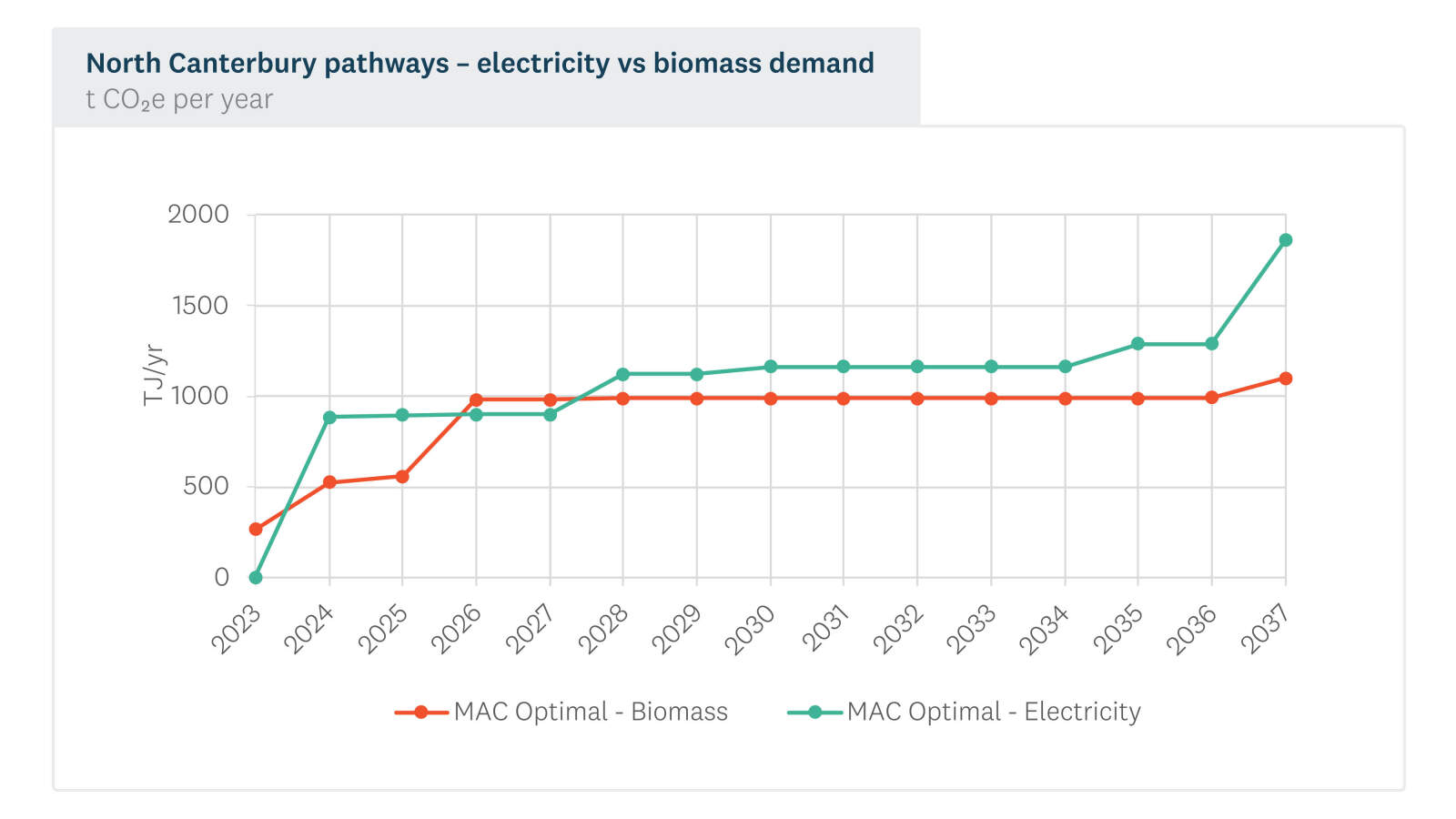
The report illustrates a range of decarbonisation pathways, all of which demonstrate how the combined decisions of a range of process heat users may lead to common infrastructure challenges and opportunities from a supply perspective. Across the 80 sites, there are 164 individual projects across demand reduction, heat pumps and fuel switching. The 'MAC Optimal' pathway sees fuel decisions that result in 62% of the energy needs supplied by electricity and 38% supplied by biomass in 2036.
Insights explored in the North Canterbury report:
-
The role demand reduction and heat pumps play in the fuel switching decision and infrastructure investment.
-
Security of electricity supply and the impact of different pathway scenarios on electricity demand.
-
Timeframes for decarbonisation under different pathway scenarios, that is:
The ‘BAU’ decarbonisation pathway, which uses the project timings in the individual ETAs (or 2036 where unavailable), is the slowest decarbonisation path. Most emissions reductions are assumed to occur in 2036.
-
The opportunity for process heat users considering electrification to reduce the costs of connection, and the total costs of purchasing electricity, by enabling flexibility in their consumption.
-
The optimisation of infrastructure investment, capacity and timing.
Read the report
Download the North Canterbury RETA report and discover the regional benefits of decarbonisation.
Read the summary report [PDF, 7.9 MB]
Spare Electrical Capacity and Load Characteristics [PDF, 7.3 MB]
The RETA process seeks to optimise infrastructure investment, capacity, and timing for the future.
Next steps and support
EECA is happy to hear from anyone wanting to support the implementation of recommendations in the North Canterbury RETA report.
Email RETA@eeca.govt.nz or kanchana.marasinghe@eeca.govt.nz with any questions.
Wayfinder
-
Co-funding opportunities
-
Explore other regions
-
Explore the RETA tool